
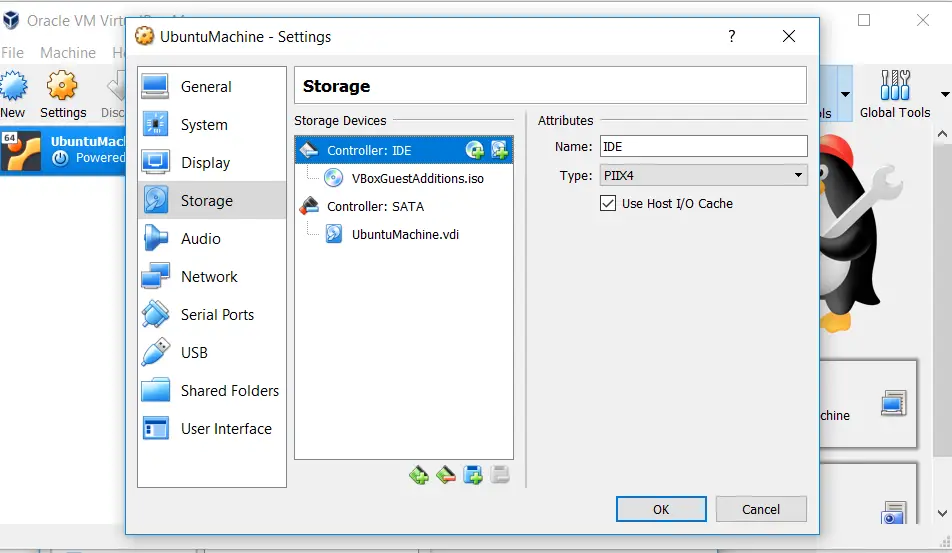
Previously I would have run through the installation process followed by customising the VM’s installed packages and installing Guest Additions before creating the base box.
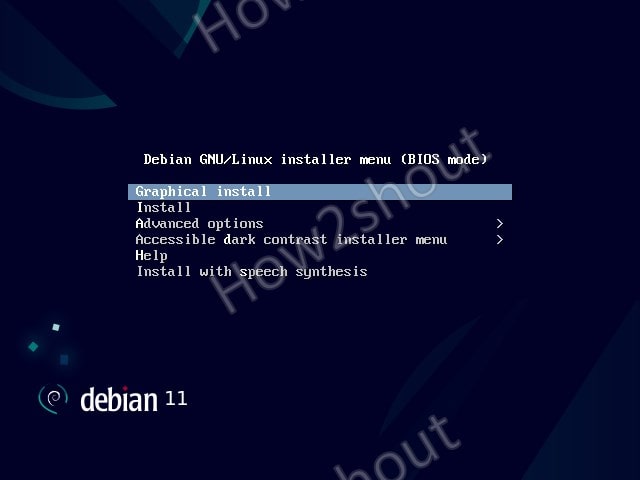
Let’s assume you want to build a new base box for Debian 11 (bullseye) to run on Virtualbox. Now install VirtualBox by executing the next command.Sometimes it might be necessary to create one’s own Vagrant base box for reasons too numerous to mention here.

Upgrade all your software by executing the next command (you can omit this step, but this may upgrade your kernel which improves the performance), then reboot your OS: sudo apt upgrade Update apt list by executing the next command: If you are using Debian 10, change bullseye to buster. Press G to go to the end of the file, then add the next line after pressing i (insert mode). Must be opened the file as root, i.e., with sudo: wget -qO-O- | sudo apt-key add -Īdd VirtualBox to apt package sources list by adding an entry to /etc/apt/sources.list file (this article will use vim the entry will be added to the end of the file). Open up a terminal either graphically or by pressing t while holding both Alt and Shift keys.Īdd the Oracle VirtualBox pgp key to apt using the following command. Installing VirtualBox via the Command-line Now you can open VirtualBox by clicking open on software install, or search for it in your app menu, or type virtualbox in terminal. Go to the download location, right-click virtualbox*.deb, then open with software install. Go to VirtualBox downloads page, click Debian 11 to download the binary package – Installing VirtualBox via the Command-line.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
